import numpy as npNumPy
- numerical python - function description
- ndarray- multidimensional array providing fast arithmetic operations
- mathematical functions
- tools for reading/writing
- linear algebra, random number generation, fourier transformation
my_arr = np.arange(1000000)
my_list = list(range(100000))%timeit my_arr2 = my_arr * 23.91 ms ± 154 µs per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 100 loops each)%timeit my_list2 = [x * 2 for x in my_list]12.3 ms ± 4.77 ms per loop (mean ± std. dev. of 7 runs, 10 loops each)data = np.array([[1.5, -0.1, 3], [0, -3, 6.5]])dataarray([[ 1.5, -0.1, 3. ],
[ 0. , -3. , 6.5]])data * 10array([[ 15., -1., 30.],
[ 0., -30., 65.]])data + dataarray([[ 3. , -0.2, 6. ],
[ 0. , -6. , 13. ]])data.shape(2, 3)data.dtypedtype('float64')# creating arrays
data1 = [6, 7.5, 8, 0, 1]
arr1 = np.array(data1)
arr1array([6. , 7.5, 8. , 0. , 1. ])data2 = [[1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8]]
arr2 = np.array(data2)
arr2array([[1, 2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7, 8]])arr2.ndim2arr2.shape(2, 4)arr1.dtypedtype('float64')arr2.dtypedtype('int32')np.zeros(10)array([0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.])np.ones((3, 6))array([[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]])np.empty((2, 3, 2))
np.arange(15)array([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14])data types for ndarrays
arr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])arr.dtypedtype('int32')float_arr = arr.astype(np.float64)float_arr.dtypedtype('float64')int_array = np.arange(10)calibers = np.array([.22, .27, .357, .380, .44, .50], dtype = np.float64)
int_array.astype(calibers.dtype)array([0., 1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8., 9.])arithmetic with numpy arrays
arr = np.array([[1., 2., 3.], [4., 5., 6.]])
arrarray([[1., 2., 3.],
[4., 5., 6.]])arr * arrarray([[ 1., 4., 9.],
[16., 25., 36.]])arr + arrarray([[ 2., 4., 6.],
[ 8., 10., 12.]])1 / arrarray([[1. , 0.5 , 0.33333333],
[0.25 , 0.2 , 0.16666667]])arr ** 2array([[ 1., 4., 9.],
[16., 25., 36.]])# comparions between arrays yield boolean arrays
arr2 = np.array([[0, 4, 1], [7, 2., 12]])
arr2array([[ 0., 4., 1.],
[ 7., 2., 12.]])arr2 > arrarray([[False, True, False],
[ True, False, True]])basic indexing and slicing
arr = np.arange(10)
arrarray([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])arr[5]5arr[5:8]array([5, 6, 7])arr[5:8]array([5, 6, 7])arrarray([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])arr_slice= arr[5:8]
arr_slicearray([5, 6, 7]) # changing values
arr_slice[1] = 12345
arrarray([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 12345, 7, 8,
9])arr_slicearray([ 5, 12345, 7])# bare slice
arr_slice[:] = 64 #assigns all values to the array
arrarray([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 64, 64, 64, 8, 9])arr2d = np.array([[1,2,3], [4,5,6], [7,8,9]])arr2darray([[[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9]]])arr2d[1]array([4, 5, 6])arr2d[0][2] #first array third element3arr2d[0,2] # same result3arr3d = np.array([[[1,2,3], [4,5,6]], [[7,8,9], [10, 11, 12]]])
arr3darray([[[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6]],
[[ 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12]]])arr3d[0]array([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])# scalar and vector arays can be assigned to arr3d[0]
old_values = arr3d[0].copy()
arr3d[0] = 42arr3darray([[[42, 42, 42],
[42, 42, 42]],
[[ 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12]]])arr3d[0] = old_values
arr3darray([[[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6]],
[[ 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12]]])arr3d[1,0]array([7, 8, 9])x = arr3d[1]xarray([[ 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12]])x[0]array([7, 8, 9])indexing with slices
arrarray([ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 64, 64, 64, 8, 9])arr[1:6]array([ 1, 2, 3, 4, 64])# slicing a 2d array
arr2darray([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9]])arr2d[:2] #selects the first two rowsarray([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])arr2d[:2, 1:] #selects first two rows and last two columnsarray([[2, 3],
[5, 6]])lower_dim_slice = arr2d[1, :2]
lower_dim_slicearray([4, 5])lower_dim_slice.shape(2,)arr2d[:2, 2] #dots before selects rows beforearray([3, 6])arr2d[:, :1] #all rows, first columnarray([[1],
[4],
[7]])# assigning value to the section
arr2d[:2, 1:] = 0arr2darray([[1, 0, 0],
[4, 0, 0],
[7, 8, 9]])Boolean indexing
names = np.array(['bob', 'joe', 'will','zhou', 'lu', 'wei' ])
namesarray(['bob', 'joe', 'will', 'zhou', 'lu', 'wei'], dtype='<U4')data = np.array([[4,7], [0,2], [-5, 6], [0, 0], [1, 2], [-12, -4], [3, 4]])
data array([[ 4, 7],
[ 0, 2],
[ -5, 6],
[ 0, 0],
[ 1, 2],
[-12, -4],
[ 3, 4]])data.shape(7, 2)names.shape(6,)# let's check how many times wei's name come
names == 'wei' #oncearray([False, False, False, False, False, True])data[names == "wei"]IndexError: boolean index did not match indexed array along dimension 0; dimension is 7 but corresponding boolean dimension is 6# adding a name so that the dimension becomes 7
names = np.append(names, 'rajwinder')namesarray(['bob', 'joe', 'will', 'zhou', 'lu', 'wei', 'rajwinder',
'rajwinder'], dtype='<U9')# deleting extra
names = np.delete(names, 7)namesarray(['bob', 'joe', 'will', 'zhou', 'lu', 'wei', 'rajwinder'],
dtype='<U9')data[names == 'rajwinder']array([[3, 4]])data[names == 'zhou']array([[0, 0]])Fancy indexing
- indexing using integers
- indexing gets modified
arr = np.zeros((8, 4))
for i in range(8):
arr[i] = iarrarray([[0., 0., 0., 0.],
[1., 1., 1., 1.],
[2., 2., 2., 2.],
[3., 3., 3., 3.],
[4., 4., 4., 4.],
[5., 5., 5., 5.],
[6., 6., 6., 6.],
[7., 7., 7., 7.]])# selecting rows in particular order
arr[[4,3, 0, 6]]array([[4., 4., 4., 4.],
[3., 3., 3., 3.],
[0., 0., 0., 0.],
[6., 6., 6., 6.]])# using negative indices
arr[[-2, -4, -7]]array([[6., 6., 6., 6.],
[4., 4., 4., 4.],
[1., 1., 1., 1.]])# multiple array indexing
arr3 = np.arange(32).reshape((8, 4))
arr3array([[ 0, 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6, 7],
[ 8, 9, 10, 11],
[12, 13, 14, 15],
[16, 17, 18, 19],
[20, 21, 22, 23],
[24, 25, 26, 27],
[28, 29, 30, 31]])# selecting elements based on rows and columns
arr3[[1, 4, 7, 2], [0, 3, 2, 1]]array([ 4, 19, 30, 9])# selecting complete rows and decding sequence of elements
arr3[[1, 4, 7, 2]][:, [0, 3, 2, 1]]array([[ 4, 7, 6, 5],
[16, 19, 18, 17],
[28, 31, 30, 29],
[ 8, 11, 10, 9]])Transposing arrays and swapping axes
arr = np.arange(15). reshape(3, 5)
arrarray([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14]])arr.Tarray([[ 0, 5, 10],
[ 1, 6, 11],
[ 2, 7, 12],
[ 3, 8, 13],
[ 4, 9, 14]])# used often for matrix computation
arrarray([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14]])# multiplied two arrays
np.dot(arr.T, arr)array([[125, 140, 155, 170, 185],
[140, 158, 176, 194, 212],
[155, 176, 197, 218, 239],
[170, 194, 218, 242, 266],
[185, 212, 239, 266, 293]])# another way to do it
arr.T @ arrarray([[125, 140, 155, 170, 185],
[140, 158, 176, 194, 212],
[155, 176, 197, 218, 239],
[170, 194, 218, 242, 266],
[185, 212, 239, 266, 293]])arrarray([[ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4],
[ 5, 6, 7, 8, 9],
[10, 11, 12, 13, 14]])arr.swapaxes(0, 1) # returns the view without making a copyarray([[ 0, 5, 10],
[ 1, 6, 11],
[ 2, 7, 12],
[ 3, 8, 13],
[ 4, 9, 14]])Pseudorandom number generation
samples = np.random.standard_normal(size= (4, 4))
samplesarray([[ 0.26762709, -0.62405293, 0.67249719, -0.46023273],
[ 0.40611368, -0.01041362, 0.51275103, -1.95844566],
[ 0.90884576, -0.28283029, 0.47254105, 2.20649657],
[ 0.69228499, -0.31918775, -0.74474035, 0.28790593]])rng = np.random.default_rng(seed = 12334)
data = rng.standard_normal((2,3))type(rng)numpy.random._generator.GeneratorUniversal Functions : Fast Element-Wise Array Functions
import numpy as np
from random import normalvariate
arr = np.arange(10)np.sqrt(arr)array([0. , 1. , 1.41421356, 1.73205081, 2. ,
2.23606798, 2.44948974, 2.64575131, 2.82842712, 3. ])np.exp(arr)array([1.00000000e+00, 2.71828183e+00, 7.38905610e+00, 2.00855369e+01,
5.45981500e+01, 1.48413159e+02, 4.03428793e+02, 1.09663316e+03,
2.98095799e+03, 8.10308393e+03])x = rng.standard_normal(8)
y = rng.standard_normal(8)
xarray([-0.32357072, -1.8494368 , -1.89739205, 0.04315429, 1.01046514,
-0.73625393, 0.46616191, -0.09290374])yarray([-0.12705798, -0.64476954, -0.62430977, 0.87432098, 1.55273649,
-1.53739177, -0.73752509, 0.41995739])np.maximum(x, y) #based on element wise comparisonarray([-0.12705798, -0.64476954, -0.62430977, 0.87432098, 1.55273649,
-0.73625393, 0.46616191, 0.41995739])arr = rng.standard_normal(7) * 5
arrarray([-1.61785359, -9.24718402, -9.48696026, 0.21577147, 5.05232568,
-3.68126964, 2.33080955])remainder, whole_part = np.modf(arr)remainderarray([-0.61785359, -0.24718402, -0.48696026, 0.21577147, 0.05232568,
-0.68126964, 0.33080955])whole_partarray([-1., -9., -9., 0., 5., -3., 2.])arrarray([-1.61785359, -9.24718402, -9.48696026, 0.21577147, 5.05232568,
-3.68126964, 2.33080955])out = np.zeros_like(arr)np.add(arr, 1)array([-0.61785359, -8.24718402, -8.48696026, 1.21577147, 6.05232568,
-2.68126964, 3.33080955])np.add(arr, 1, out= out)array([-0.61785359, -8.24718402, -8.48696026, 1.21577147, 6.05232568,
-2.68126964, 3.33080955])outarray([-0.61785359, -8.24718402, -8.48696026, 1.21577147, 6.05232568,
-2.68126964, 3.33080955])Array oriented programming with Arrays
- vectorization (faster) than pure Python equivalents
points = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.01) #100 equally spaced points
xs, ys = np.meshgrid(points, points)
# numpy.meshgrid function takes two one-dimensional arrays and produces two two-dimensional matrices
ysarray([[-5. , -5. , -5. , ..., -5. , -5. , -5. ],
[-4.99, -4.99, -4.99, ..., -4.99, -4.99, -4.99],
[-4.98, -4.98, -4.98, ..., -4.98, -4.98, -4.98],
...,
[ 4.97, 4.97, 4.97, ..., 4.97, 4.97, 4.97],
[ 4.98, 4.98, 4.98, ..., 4.98, 4.98, 4.98],
[ 4.99, 4.99, 4.99, ..., 4.99, 4.99, 4.99]])z = np.sqrt (xs ** 2 + ys ** 2)
zarray([[7.07106781, 7.06400028, 7.05693985, ..., 7.04988652, 7.05693985,
7.06400028],
[7.06400028, 7.05692568, 7.04985815, ..., 7.04279774, 7.04985815,
7.05692568],
[7.05693985, 7.04985815, 7.04278354, ..., 7.03571603, 7.04278354,
7.04985815],
...,
[7.04988652, 7.04279774, 7.03571603, ..., 7.0286414 , 7.03571603,
7.04279774],
[7.05693985, 7.04985815, 7.04278354, ..., 7.03571603, 7.04278354,
7.04985815],
[7.06400028, 7.05692568, 7.04985815, ..., 7.04279774, 7.04985815,
7.05692568]])# visualizations with 2-d arrays
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.imshow(z, cmap = plt.cm.gray, extent = [-5, 5, -5, 5])
plt.colorbar()
plt.title("Image plot $\sqrt{x^2 + y^2}$ for a grid of values")Text(0.5, 1.0, 'Image plot $\\sqrt{x^2 + y^2}$ for a grid of values')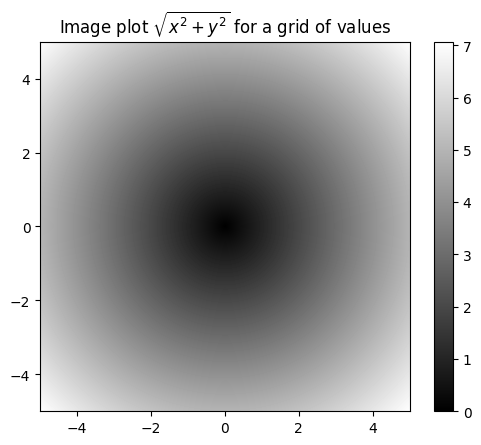
plt.close('all')Expressing Conditional Logic as Array Operations
xarr = np.array([1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5])
yarr = np.array([2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4, 2.5])
cond = np.array([True, False, True, True, False])# take value form xarr whenever true, otherwise take value from yarr
result = [(x if c else y)
for x, y, c in zip (xarr, yarr, cond)]result[1.1, 2.2, 1.3, 1.4, 2.5]numpy.where
# numpy.where (replace all positive values with 2 and negative with -2)
arr = rng.standard_normal((4, 4))
arrarray([[-0.09290374, -0.12705798, -0.64476954, -0.62430977],
[ 0.87432098, 1.55273649, -1.53739177, -0.73752509],
[ 0.41995739, -0.93658739, 0.62072248, 0.81057914],
[-0.21398203, 0.67748945, -1.54002066, -0.9638457 ]])arr > 0array([[False, False, False, False],
[ True, True, False, False],
[ True, False, True, True],
[False, True, False, False]])np.where (arr > 0, 2, -2)array([[-2, -2, -2, -2],
[ 2, 2, -2, -2],
[ 2, -2, 2, 2],
[-2, 2, -2, -2]])# or set only the positive values to 2
np.where (arr > 0, 2, arr)array([[-0.09290374, -0.12705798, -0.64476954, -0.62430977],
[ 2. , 2. , -1.53739177, -0.73752509],
[ 2. , -0.93658739, 2. , 2. ],
[-0.21398203, 2. , -1.54002066, -0.9638457 ]])mathematical and statistical methods
arr = rng.standard_normal ((5, 4))
arrarray([[-0.64316368, -0.48860061, -1.41271857, -0.10120962],
[-0.70385422, 2.41319157, -0.54405393, -0.90339244],
[ 0.82712685, -0.62647321, -0.13480887, 0.03956079],
[ 0.56044129, 0.34237924, -0.6576538 , 1.04696188],
[ 0.17595271, -1.13639865, -0.54922125, 0.70725439]])arr.mean()-0.08943400646176203np.mean(arr)-0.08943400646176203arr.sum()-1.7886801292352406arr.mean(axis = 1) # columnsarray([-0.66142312, 0.06547274, 0.02635139, 0.32303215, -0.2006032 ])arr.sum(axis = 1)array([-2.64569248, 0.26189098, 0.10540556, 1.29212861, -0.8024128 ])arr = np.array([0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7])
arr.cumsum()array([ 0, 1, 3, 6, 10, 15, 21, 28])arr = np.array([[0,1,2], [3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8]])
arrarray([[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5],
[6, 7, 8]])# arr.cumsum(axis = 0 ) computes the cumulative sum along rows
# arr.sumsum (axis= 1) computes the sum along columns
arr.cumsum(axis = 0)array([[ 0, 1, 2],
[ 3, 5, 7],
[ 9, 12, 15]])arr.cumsum(axis = 1)array([[ 0, 1, 3],
[ 3, 7, 12],
[ 6, 13, 21]])methods for boolean arrays
arr = rng.standard_normal(100)
(arr> 0).sum()41(arr <= 0).sum() #all non-po59Sorting
arr = rng.standard_normal(6)
arrarray([ 0.81272428, -0.67629236, 0.09344394, -0.20621744, 0.10364886,
0.70966403])arr.sort()arrarray([-0.67629236, -0.20621744, 0.09344394, 0.10364886, 0.70966403,
0.81272428])arr = rng.standard_normal((5, 3))
arrarray([[-1.58684863, -0.1143117 , 2.38420916],
[-0.64811009, 1.31931176, 0.01123432],
[-0.90663373, -0.96531814, 0.46431808],
[ 0.52164015, -0.08486576, -0.98397298],
[ 0.09054187, -1.08417551, -0.48832961]])arr.sort (axis = 0) #sorts the values across columns
arrarray([[-1.58684863, -1.08417551, -0.98397298],
[-0.96531814, -0.90663373, -0.48832961],
[-0.64811009, -0.1143117 , 0.01123432],
[-0.08486576, 0.09054187, 0.46431808],
[ 0.52164015, 1.31931176, 2.38420916]])arr.sort (axis = 1)
arrarray([[-1.58684863, -1.08417551, -0.98397298],
[-0.96531814, -0.90663373, -0.48832961],
[-0.64811009, -0.1143117 , 0.01123432],
[-0.08486576, 0.09054187, 0.46431808],
[ 0.52164015, 1.31931176, 2.38420916]])arr2 = np.array([5, -10, 7, 1, 0, -3])
sorted_arr2 = np.sort(arr2)
sorted_arr2array([-10, -3, 0, 1, 5, 7])unique and other set logic
namesarray(['bob', 'joe', 'will', 'zhou', 'lu', 'wei', 'rajwinder'],
dtype='<U9')np.unique(names)array(['bob', 'joe', 'lu', 'rajwinder', 'wei', 'will', 'zhou'],
dtype='<U9')np.append(names, 'lu')array(['bob', 'joe', 'will', 'zhou', 'lu', 'wei', 'rajwinder', 'lu'],
dtype='<U9')# we've 'lu' twice now, let's see now unique
# sorting done aswell
np.unique(names)array(['bob', 'joe', 'lu', 'rajwinder', 'wei', 'will', 'zhou'],
dtype='<U9')# python alternative
sorted(set(names))['bob', 'joe', 'lu', 'rajwinder', 'wei', 'will', 'zhou']array set operations
# numpy.in1d for testing memebership of the values in one array
values = np.array([6, 0,0,0,3,2])
np.in1d(values, [1,2,3])array([False, False, False, False, True, True])file input and output
arr = np.arange(10)np.save('some_array', arr)np.load('some_array.npy')array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])# save multiple arrays using np.savez
np.savez('array_archive.npz', a = arr, b=arr)arch = np.load("array_archive.npz")arch['b']array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])# saving in compressed format
np.savez_compressed('arrays_compressed.npz', a= arr, b= arr)Linear Alzerba
x = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
y = np.array([[6, 23], [-1, 7], [8,9]])
xarray([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6]])yarray([[ 6, 23],
[-1, 7],
[ 8, 9]])x.dot(y)array([[ 28, 64],
[ 67, 181]])# equivalent to
np.dot(x, y)array([[ 28, 64],
[ 67, 181]])# product of 1d and 2d array
x @ np.ones(3)array([ 6., 15.])# numpy.linalg (matrix decompositions)
from numpy.linalg import inv, qr
X = rng.standard_normal((5, 5))
mat = X.T @ Xmatarray([[ 5.79511464, -3.30831545, -2.66542844, -0.61858429, -4.34315368],
[-3.30831545, 6.04913293, 1.09484984, -0.88187098, 3.79344801],
[-2.66542844, 1.09484984, 3.59693921, -0.10949232, 1.50109261],
[-0.61858429, -0.88187098, -0.10949232, 0.68764721, 0.24806815],
[-4.34315368, 3.79344801, 1.50109261, 0.24806815, 4.09980802]])inv(mat)array([[ 1.95391205, 0.4259796 , 0.86161239, 1.99396982, 1.23962108],
[ 0.4259796 , 1.84110512, 0.55359754, 3.43225775, -1.66263314],
[ 0.86161239, 0.55359754, 0.79117237, 1.60608307, 0.01366661],
[ 1.99396982, 3.43225775, 1.60608307, 8.69084511, -2.17736422],
[ 1.23962108, -1.66263314, 0.01366661, -2.17736422, 3.22224774]])mat @ inv(mat)array([[ 1.00000000e+00, 7.37690538e-17, 8.63526934e-17,
2.45602532e-16, 5.57110698e-16],
[ 3.59505366e-17, 1.00000000e+00, -1.43602651e-16,
1.56181454e-15, -8.26684003e-16],
[-2.51848975e-16, -9.56323491e-18, 1.00000000e+00,
-7.81952475e-16, -4.32942875e-16],
[-1.22081410e-16, 5.77266093e-17, -3.23653576e-16,
1.00000000e+00, -9.26541377e-18],
[-4.93401745e-16, 1.63171237e-15, -7.64319458e-17,
1.26774536e-15, 1.00000000e+00]])Random walks
# with python
import random
position = 0
walk = [position]
nsteps = 1000
for _ in range(nsteps):
step = 1 if random.randint(0, 1) else -1
position += step
walk.append (position)plt.plot(walk[:100])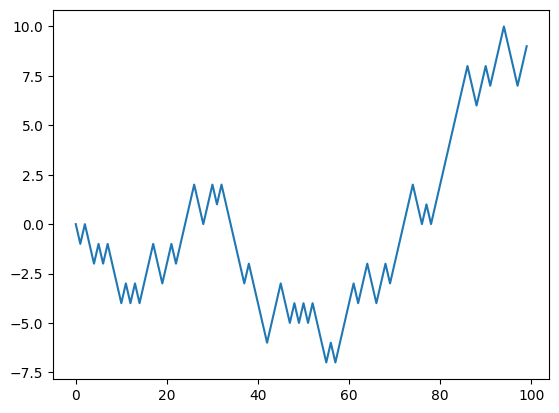
# with numpy
nsteps = 1000
rng = np.random.default_rng (seed = 12345)
draws = rng.integers(0, 2, size= nsteps)
steps = np.where(draws == 0, 1, -1)
walk = steps.cumsum()walk.min()-8walk.max()50(np.abs(walk) >= 10).argmax()155# simulting many random walks at once with numpy
nwalks = 5000
nsteps = 1000
draws = rng.integers(0, 2, size = (nwalks, nsteps))
steps = np.where(draws > 0, 1, -1)
walks = steps.cumsum(axis = 1)
walksarray([[ 1, 2, 1, ..., -24, -25, -26],
[ -1, 0, -1, ..., -2, -1, 0],
[ 1, 0, 1, ..., -22, -23, -24],
...,
[ 1, 0, 1, ..., 0, 1, 0],
[ -1, -2, -3, ..., 78, 77, 78],
[ 1, 2, 1, ..., -42, -41, -40]])walks.max()143walks.min()-125# any method to check for details
hits30 = (np.abs(walks) >=30).any(axis = 1)
hits30array([ True, False, True, ..., False, True, True])hits30.sum()3314crossing_times = (np.abs(walks[hits30]) >= 30).argmax(axis = 1)
crossing_timesarray([897, 187, 607, ..., 497, 363, 337], dtype=int64)# average minn